
 Downloads
DownloadsTri-Mer Filters for NOx Reduction (DeNOx)
To remove NOx, catalytic ceramic filter elements are manufactured with nano-bits of SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst embedded in the walls, about 3/4 inch (20 mm) thick. These filters achieve NOx removal with over 90% efficiency.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is the process of NOx reduction, or DeNOx, that occurs when a NOx source is mixed with ammonia (or other agent) and allowed to react at the surface of a catalyst. Selection of an appropriate technique will depend on the type of facility (boilers, gas turbines, incinerators), site-specific conditions, and regulatory considerations.
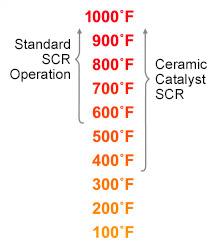
The lower operating temperature of the UltraCat Catalytic Filter Systems contrasts favorably with devices such as SCR used for NOx control.
The liquid urea or ammonia is injected upstream of the filters and turns into gas, mixes with the NOx gas, allowing the mixture to react at the catalyst. The result is conversion to nitrogen gas N2 and water vapor H2O, both harmless constituents of the atmosphere. While the process uses aqueous ammonia, there is no wet residue or by-product. All the reactants leave the system as gases.
Tri-Mer offers 4 DeNOx methods: |
||
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Dry removal with the unique ceramic catalyst filters for gas temperatures greater than 350°F. This technology features DeNOx at temperatures lower than conventional SCR while also capturing particulate, and offers the option of removing acid gases, mercury, and dioxins. |
| 2 |  |
Conventional stand-alone SCR equipment for low temperature NOx reduction that operates at roughly 300°F – 750°F. |
| 3 |  |
High temperature DeNOx that operates in the range of 600°F to 1100°F to achieve high levels of effectiveness while consuming reasonable quantities of catalyst material. |
| 4 |  |
A non-SCR process, wet scrubbing with the Tri-NOx NOx scrubber, for applications under 350°F with special requirements. |
NOx reduction efficiencies over 90% can be achieved. Tri-Mer integrated SCR systems, whether filter based or stand-along catalytic reactor, include ammonia injection and storage tanks. For smaller applications, 300-gallon totes of aqueous ammonia are suitable.
NOx reduction at lower temperatures solves many difficult pollution control problems. It eliminates the need to heat the gas if the source cannot supply sufficient temperature for conventional high-temp SCRs.
Tri-Mer low-temp NOx reduction systems operate at approximately 300°F – 750°F, and become effective at 300°F, with efficiency climbing very high as the temperature increases. These systems are well suited for boilers, incinerators, and similar applications.
All SCR systems must have inlet streams that are free of particulate. Particulate blocks the reaction sites and can chemically alter catalytic reactions. Being fouled with PM is the leading cause of short catalyst life and performance failures. In the case of the ceramic catalyst filters, the micronized catalyst is inside the walls of the filter and thus protected from particulate.
Low-temp UltraSCR catalyst blocks.
Ceramic filters capture particulate on the outer surface, with negligible penetration to the interior of the filter media. In contrast, a stand-alone low-temp SCR system must be downstream of some form of effective PM removal.
Besides the need for high temperature, a common problem with traditional SCR is that the catalyst becomes poisoned and ineffective, necessitating early replacement. Typical poisons are ordinary PM, metals, and HCl.
Because our micronized catalyst is surrounded by filter material, it is almost 100% protected from blinding. When combined with acid gas removal using dry sorbent injection, other poisons like HCl, along with SO2, are removed at very high rates. In addition, the catalytic filter has a proprietary chemistry that results in a fraction of the conversion rate of SO2 to SO3 seen with traditional SCR catalysts. NOx control that extends the catalyst life to 5 years, 10 years, or beyond, is a revolutionary advantage.
The increased reactivity shown by the catalytic filters at lower temperatures results, in part, from their micronized form. The diffusion restriction is eliminated, unlike conventional big-block SCR where diffusion is a major restriction. Ammonia slip is less than 5 ppmv, and generally less than 2 ppmv. NOx control that reaches high removal efficiency with minimum ammonia slip is a revolutionary advantage.

Aqueous ammonia used on smaller DeNOx projects.

DeNOx filling station and storage tanks used on large DeNOx installations.
• Particulate (PM 10, PM 2.5, PM 1.0) • NOx • SOx (SO2, SO3) • HCl, HF • Metals (Selenium, Arsenic …) • Mercury • Hexavalent Chrome • Dioxins / Furans • Selective VOC (Cement O-HAPS) • Add-on CO module available