Your Questions re: Wet Scrubbers
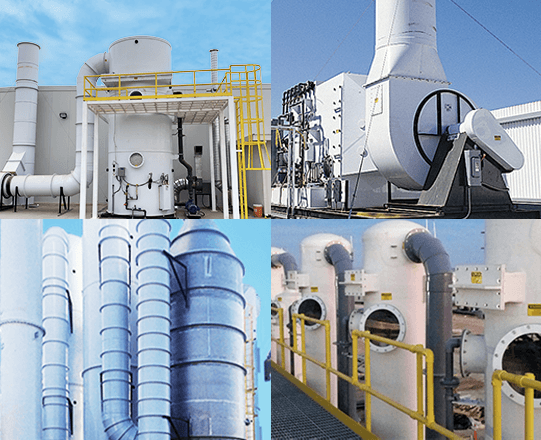

According to EPA, a wet scrubber air pollution device removes PM and acid gases from the waste gas streams of stationary point sources. Pollutants are removed through impaction, diffusion, interception or absorption of the pollutant onto droplets of liquid. Tri-Mer offers several wet scrubbers that efficiently remove both acid gas and particulate, including PM10 and PM2.5.
Q. Can Tri-Mer specify an exhaust system with scrubbing capability for our steel pickling operation?
A. Tri-Mer has extensive design capabilities for scrubbers and scrubber exhaust systems to control acid/alkali fumes and other droplets and gas phase contaminants from steel pickling and other metal finishing processes. Tri-Mer systems are guaranteed to operate with zero stack opacity, and with no process residues outside the stack. We’d be glad to assist in designing a system tailored to your needs and budget.
Q. A scrubber is connected to our anodizing line, and two of the tanks are not getting good capture. Would it be better to add a small push system, or are there better options for boosting airflow on the far end of the ducting?
A. While each application is unique, there are several considerations when troubleshooting poor exhaust capture: Industry standards recommend a minimum exhaust flow rate of 100 acfm/ft2 for push-pull ventilation configurations, while laterial exhaust only (no push assist) requires 250 acfm/ft2 in most cases. (Per Industrial Ventilation A Manual of Recommended Practice for Design, 31st Edition, ACGIH). Given this, a push air header may be a good solution for improving source capture without increasing the overall exhaust volume of the system.
In any case, the complete system should be analyzed from a design standpoint to qualify any modifications.
This form is the fastest way to get in touch with us.
A more detailed form, located here, will tell us what we need to generate a detailed quote.